Weight loss
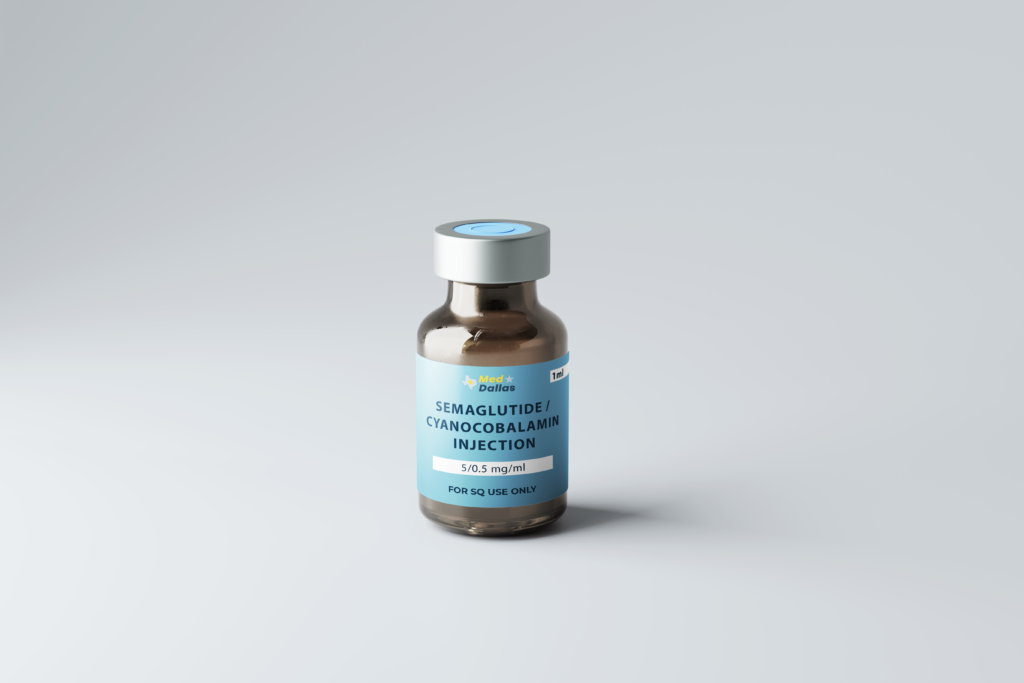
Semaglutide / Cyanocobalamin Injection
Discover the benefits of Semaglutide/Cyanocobalamin Injection, available exclusively through our 503A Compounding Pharmacy. Semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, is designed to aid in weight loss and manage Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, while Cyanocobalamin supports essential vitamin B12 levels. Explore how this powerful combination can enhance your health journey, with insights into usage, benefits, and safety considerations.
